 |
|
||||||||
|
|||||||||
|
 |
|
||||||||
|
|||||||||
|
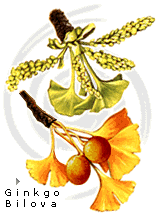 Ginkgo The ginkgo is the only survivor of an old family of trees, the Ginkgoes, widely spread at the beginning of geological times and with a broad representation between fossils, are the nexus between ferns and superior plants. Although nowadays it is only native of the China province of Chekiang, the ginkgo is frequently planted as ornamental tree in all the temperate zones, where it reaches a height of 30 m. It is caducous and in autumn, before falling, the leaves acquire a beautiful golden shade; in winter, the thin and lanky crowns of the young trees with its long and bare branches and the side short and irregular branches are very characteristic, although with the age they turn broader and rounder. The foliage is notably similar to the fronds of the maidenhair tree, although in China is called 'duck feet tree' referring also to the form of its leaves. The brown-reddish buds, are helicoidal arranged over the peduncles, when the leaves appear they are completely yellow, but turn green as they open, and at the end they are coriaceous, fan-shaped with a notch in the apex and variable dimensions 6-10 x 4-8 cm. Their clearly visible nerves are opened radially from the base, and the petioles to 4 cm are helicoidally placed over the new stalks, but over the old ones they form verticils or racemes on short spurs. Almost all the trees are males, with groups of yellowish catkins of 5-7 cm long. In the few female trees the small ovoid green flowers, that appear in groups of two or three, but each with its corresponding peduncle of 2-5 cm long, are turned into pulpy fruits similar to small plums of 2-3,5 cm long, green first, but yellow-orange when ripen, and with an intense stink when they are rotten. The seeds are edible and in China, where they are sold with the name of 'Pai-Kwo', are very estimated to be roasted. The ginkgo wood is yellow, light, easily broken and no valuable, although Chinese and Japanese use it for small carving. The trunks are deeply channeled and the grayish bark is quite suberized, with wide irregular fissures that are divided in unequal layers, with frequent protuberances and burrs. Encyclopedia BLUME, Trees, wood and forests of the world, H. Edlin/M.Nimmo, page 86. |
| 3/4/2014 5:35:27 PM |
|
| Rama Forestry Project - Estancia Rama - Provincial Route 9 Km. 72 - Valle of Pancanta -
(5701) San Luis - Argentina / TE: +54 2652 447480 / +54 2652 452000 ext 4308
rama@rama.com.ar
| |